 The most important work of all entrepreneurs is optimizing their business so that it will be more efficient, scalable, and cost-effective. And the best way to do this is through Odoo implementation – the integration of Odoo, a powerful open-source ERP system, into business processes.
The most important work of all entrepreneurs is optimizing their business so that it will be more efficient, scalable, and cost-effective. And the best way to do this is through Odoo implementation – the integration of Odoo, a powerful open-source ERP system, into business processes.
Implementation of Odoo refers to the process of integrating the Odoo ERP software into a business to automate operations. It includes planning, module setup, workflow configuration, data migration, testing, and training the users on how best the system serves them.
Odoo ERP Implementation isn’t something that can be done overnight. With proper planning, a careful setup can actually make it a great tool for an organization. This Odoo implementation guide covers every detail for you to set up Odoo, install it, configure it, and tune it to the precise requirements of your business.
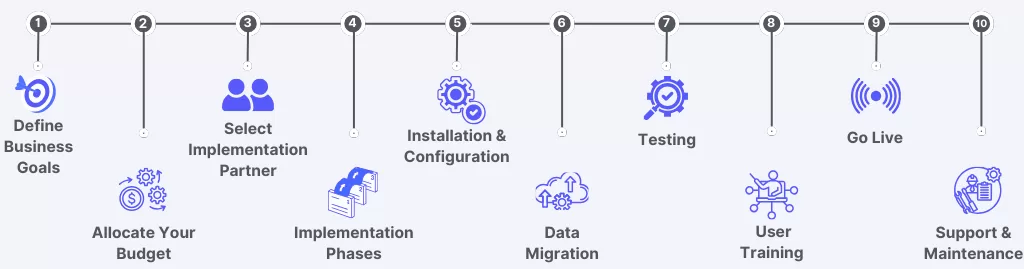
Step 1: Planning Your Odoo Implementation
Before learning about the technicalities of Odoo, it is important to lay a strong foundation. A well-thought-out Odoo implementation guide will not only direct your setup process but also ensure that the implementation aligns with your business objectives.
Define Clear Business Objectives
First start defining for what purpose one actually wants the software installed – inventory management, linking accounts processing, or something on improving CRM. With a clear Odoo implementation guide, it’s easy for any client to define the correct priority settings and modules developed.
Understand the Modules You Need
There are more than 30 modules of Odoo for different business functions. You might not require all of them. For example, for an e-commerce website, you might require Sales, Inventory, Accounting, CRM, and Website. Successful Odoo ERP implementations focus on rolling out the most relevant modules first to maximize early impact.
What is more crucial during our implementation process, however, is to find modules that can directly contribute more significantly and further to core activities of actual use in daily life. Therefore, your Odoo implementation guide should help you evaluate which modules make immediate sense and drive value in daily operations. Roll these modules out incrementally for smoother adoption.
Identify and Evaluate Existing Processes
Take the time to understand the systems you are using today along with integration points to Odoo. Whether it is your website, CRM, or accounting software, some areas should be noted at this stage.
Step 2: Preparing for Odoo Implementation
The implementation process involves all sides’ preparation, that is, choosing either a cloud or on-premises to assemble the implementation team as well as to plan for the migration of data.
Choosing between Odoo Cloud or On-Premise
The first big decision you will have to make is to opt for Odoo Cloud or install on-premise. Generally, Odoo Cloud is less burdensome in terms of implementation and maintenance, especially for businesses without an internal IT team; it costs less too, since Odoo itself administers server administration and issues security updates.
While you control all data in an on-premise deployment, the primary reason it is preferred is that you have complete control over data. For specific customization needs and certain business-related reasons due to privacy over data for your organization, a totally on-premise environment does make complete sense.
Build Your Implementation Team
A successful implementation is not a one-person show. You will require a strong, adequate team to manage the Odoo project, whether internally or through an experienced Odoo consultant.
Data Migration Planning
All old system data from customers should be transferred to Odoo. Such include the stocks and historical financials, among other important historical data. The actual import of data starts only when you’ve fully moved this information.
Plan a Realistic Timeline and Budget
Realistically estimate how long each phase of the Odoo ERP implementation will take. If the module to be implemented is a single one or if heavy customization is required, then the time has to be stretched. Add the training and consulting costs in addition to the costs of any kind of customization.
Step 3: Setting up Odoo
It is time to configure Odoo once you’ve prepared your team and business for the implementation.
Odoo Setup and Installation
Whether you have it on the cloud or on your own servers, it’s all about starting with installation. Fortunately, the installation for Odoo’s cloud is not very complicated at all. Once installed, you are going to make a few basic configurations that would require adding company details and configuring fiscal years.
One thing I have learned over the years is that the localization settings, which include tax rates, currencies, and language preferences, must be set up in the right way. All the above applies highly to organizations operating in different regional areas.
Setup User Roles and Permissions
You can then make different roles and assign varying degrees of access to them; for example, managers will be granted access to data from the sales side of the business, but a sales representative will only be granted access to information related to customers and their orders.
Role-based access control has been central in ensuring sensitive data becomes available to whoever needs it. However, all this should be ensured and done in a manner that promotes security.
Module Configuration
Now that you have Odoo installed, the next step is to configure your modules based on your needs. Each module has a huge setting, where you can customize each to suit your business process. I would first recommend basic modules like Sales, Inventory, and Accounting.
All should be well-integrated so that the impact of the change from one module positively affects another. For example, using the Inventory module in Odoo, when there was the need for adjustment in order to reflect an inventory tracking system with categories of products needed to adjust stock levels from all sales passing through.
Step 4: Customizing Odoo for Business Needs
The system is truly very flexible; you can really make strong customization, whether on workflows or additional custom fields. Customization ensures that you’re given exactly what you need. A comprehensive Odoo implementation guide should always factor in these customization opportunities from the start.
Customizing the Interface
The self-crafted dashboard with current lead, opportunity, or sales performance data, according to my experience, made a real difference when increasing productivity. An effective Odoo implementation guide should walk you through how to tailor the interface to match your team’s working style.
Building Custom Workflows
Workflows help you automate processes and ensure things run more efficiently for you. For instance, you may want to create a workflow that automatically sends a sales order to generate an invoice or automatically sets a stock update once sold.
Customized workflows that we had designed for one of our clients would automatically refresh stock levels as the product was shipped and re-order the product, saving countless man-hours tracking this manually.
Step 5: Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing is the implementation phase to be executed. The test will be performed before an Odoo goes live. There are various phases involved in the testing process so that everything goes through smoothly.
Pre-Go Live Testing
You will want to do functional and integration testing before going live across your whole business. You want to make sure all your modules are working properly and test your integrations. Also, ensure that shipping modules and payment gateways are all working smoothly.
Especially on activities of migration on large data volumes, that you ought to do multiple rounds of testing. One thing that’s just unacceptable is to go live with outstanding problems.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
UAT testing is conducted on real users in a manner that assures the system addresses the particular needs of those using the system. It will, therefore, need real user responses to be confident of being intuitive and functional.
Step 6: Training and Support for Odoo Users
It is definitely going to require good training and support for your team in order to easily adopt the new system.
User Training
Schedule some training sessions for your staff to be familiar with the Odoo module functionalities. The need for the kind of training will depend on the kind of user, for instance, the sales team, the manager, and the accounting staff.
Create a Support Plan
After the installation, you will support your team. This could be an in-house support team or any set of external consultants that help solve issues as they come up. With this in place, at my company, we had an Odoo support channel where all the issues were inputted to be fixed on the spot, which otherwise would have been a massive disruption in the beginning stage of adoption.
Step 7: Going Live and Post-Implementation
The final step to implement Odoo is after all planning, preparation, and customization: it is time to go live.
Final Preparations
This stage involves checking for configurations and permissions for users, as well as data migration. All stakeholders must be communicated to use the system.
Go Live
When the system is ready to go live, the team should be ready to handle the issues that arise. The system has to be closely monitored with extra training in case it necessitates so.
Post-Go Live Optimization and Monitoring
Even after going live, make sure to keep monitoring the performance of your system. Get feedback from your team and identify the areas of improvement.
Conclusion
A successful Odoo ERP implementation isn’t just about installing software – it’s about transforming how your business works. This comprehensive Odoo implementation guide walks you through planning, configuring, customizing, and optimizing Odoo to make your business more efficient and scalable.
Thus, by following these steps, from defining your business objectives to going live and optimizing post-implementation, your things will go smoothly and successfully. It unlocks real potential when one takes their time and properly plans, configures, tests, and trains their team.


Odoo One App vs. Odoo Standard vs. Odoo Custom: Which Odoo Variant is best for your business? | HSxTech
December 3, 2024[…] edition: Organizations can take advantage of this version. The open-source community version includes the most important and mandatory functionalities […]